MTH211 Foundations of Elementary Math 1

Fun with whole numbers.
Table of Contents
- Chapter 1: Problem Solving
- Chapter 2: Sets and Reasoning
- Chapter 3: Whole Numbers
- Chapter 4: Number Theory
- Factors and Multiples
- Greates Common Factor and Lowest Common Multiple
§ 3.2 Addition and Subtraction
Math Activity 3.2: Playing with Blocks
Addition with base-ten blocks
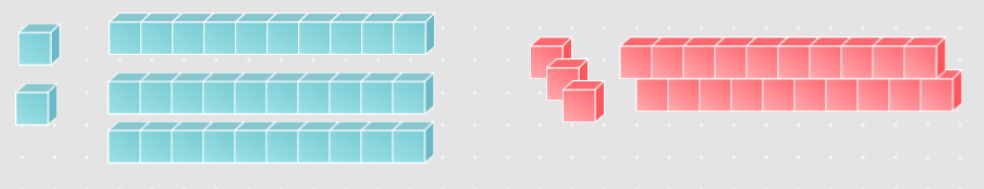
Math Activity 3.2: Playing with Blocks
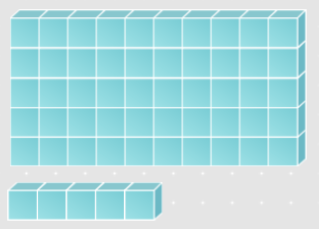
Subtraction with base-ten blocks
36 - 23 means, what do you get if you take 23 away from 36?
So, start with 36:
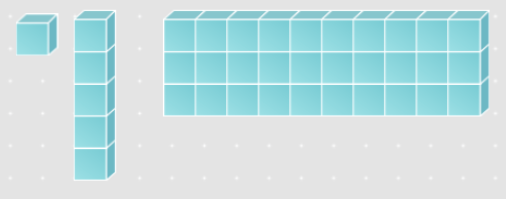
Now, take away 23:
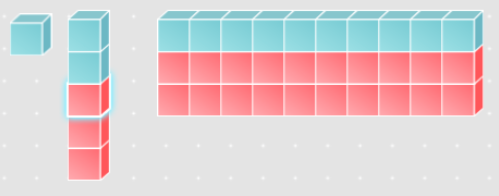
That leaves 13!
Main topics
- Addition Models
- set model
- number line model
- Addition Properties
- closure
- Commutative
- Associative
- identity
- Addition Algorithms
- standard (right to left, regroup)
- Expanded
- Lattice
- Hindu (left to right)
- Inequality
- Subtraction Models
- Take-away
- Compare
- Missing Addend (what do I add?)
- number line
- Subtraction Algorithms
- Standard (right to left, rename)
- Equal Additions
- Hindu (left to right)
- Complements
- Subtract up
- low stress
- Approximations and Estimations
- Front end
- Compatible numbers
§ 3.3 Multiplication
Math Activity 3.3: Multiplication as Area
Main Topics
- Multiplication Models
- Groups of
- Repeated Addition
- Area
- Array
- Cartesian Product
- Factors
- Products
- Partial Products
- Algorithms
- Repeated addition
- Expanded
- Regrouping (Standard)
- Hindu (left to right)
- Lattice
- Properties
- Closure
- Commutative
- Associative
- Identity (one)
- Distributive property of multiplication over addition
- Estimation
§ 3.4 Division and Exponents
Math Activity 3.4: Division Models
Check out section 3.4 of the book, Division and Exponents. There are 2 models listed:
1. The Set Partition Model (sharing concept)
2. The Repeated Subtraction Model (measurement concept)
For each of these illustrate and explain 42/3. Your illustrations should be similar to those in the book for Example D, 48/4.
Main topics
- Definition of division:
If `n-:d=q`, then `q*d=n`
`6-:2=3` since `3*2=6` - Division Models
- Set Partition
Split 6 into 2 groups. How many are in each group?
- Repeated Subtraction
How many groups of 2 are in 6?
- Missing Factor (aka what do I multiply by?)
`6-:2=square` means `square xx 2 = 6`
- Set Partition
- Division Algorithms
- Repeated Subtraction
- Grouped Repeated Subtraction
- Scaffolding
- Long Division
- Short Division
- Division Algorithm Theorem
For any whole numbers `n` and `d`, with divisor `d!=0`, there are whole numbers `q` and `r` such That- `n=d*q+r`
- `0≤r<d`
- Division with zero
- `0//3=0`
- `3//0` is undefined
- `0//0` is indeterminate
- Equal quotients
`70-:20=7-:2=3 1/2` - Approximate quotients and compatible numbers
`31-:16~~30-:15=2` - Rounding and front-end estimation
`723-:215~~700-:200=7-:2=3 1/2` - Exponents
- `b^0=1` show pattern
- `b^1=b` show pattern
- `a^n*a^m=a^(n+m)`
- `a^n/a^m=a^(n-m)`
- `(a^n)^m=a^(n*m)`
- `(a*b)^n=a^n*b^n`
- `(a/b)^n=a^n/b^n`
- Scientific Notation
- Order of Operations
- Parentheses (inside)
- Exponents
- Multiplication OR Division (left to right)
- Addition OR Subtraction (left to right)
Chapter 4: Number Theory
§ 4.1 Factors and Multiples
Math Activity 4.1: ?
§ 4.2 Greatest Common Factor and Least Common Multiple
Math Activity 4.2: ?